Ergonomic Tips for Computer Users
Overview
Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people, their work tasks, and their physical work environment. It attempts to reduce strain, fatigue, and injuries by improving product design and workspace arrangement. The goal is a comfortable, relaxed posture.
Many people spend hours a day in front of a computer without thinking about the impact on their bodies. They physically stress their bodies daily without realizing it by extending their wrists, slouching, sitting without foot support and straining to look at poorly placed monitors.
These practices can lead to cumulative trauma disorders or repetitive stress injuries, which create a life-long impact on health. Symptoms may include pain, muscle fatigue, loss of sensation, tingling and reduced performance.
Compare These Two Workstations

Adapt Your Workspace
Posture And Positioning
- Maintain good posture when working at the keyboard. Utilize a chair with back support.
- Keep your feet supported on the floor or on a footrest when you work to reduce pressure on your lower back
- Avoid twisting or bending your trunk or neck. Frequently used items should be positioned directly in front of you and angled upward on a copyholder when working.
- Keep your shoulders relaxed with your elbows close to your sides.
- Avoid resting your elbows on the hard surface or edge of your table. Pads can be used to protect your elbows if necessary.
- Elbows should be positioned at 100 to 110 degrees when working in order to keep a relaxed position at the keyboard. This could require a slight negative tilt (front of keyboard higher than back) when working in upright positions. If reclined in your chair, the keyboard could be at a positive angle to maintain this relaxed position.
- Your wrists should be in a neutral or straight position when keying or using a pointing device or calculator. Wrist rests can assist you in maintaining a neutral position when used properly during pauses. Float your arms above the keyboard and wrist rest when keying. Avoid planting your wrists on the table or wrist rest. This can result in bending the wrists either up and down or side to side.
- Take breaks. These breaks can be brief and should include stretches for optimal results. If possible, take a one or two-minute break every 15 to 20 minutes, or a five-minute break every hour. Every few hours, get up, move around, and do an alternative activity.
Laptop Considerations
Laptop computers are not ergonomically designed for prolonged use. The monitor and keyboard are so close together that they cannot both be in good positions at the same time. For prolonged use, it’s best to add a separate monitor and keyboard. The laptop can be planced on books so the top of the screen is at eye level, then use an external keyboard so that your elbows can rest at 90° by your side.
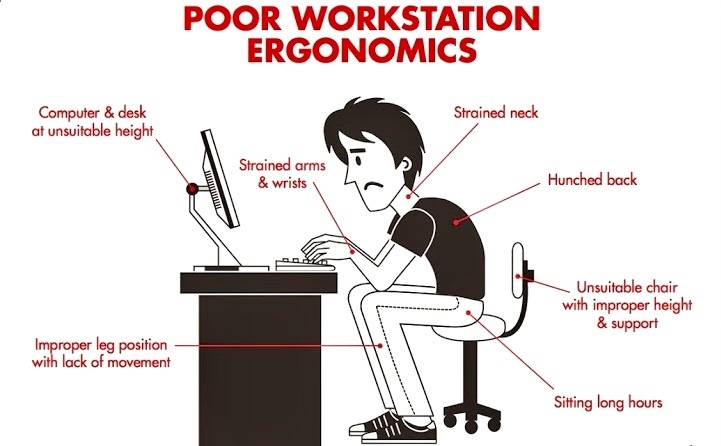
Don't be THIS guy

So tell us YOUR story!
Ask questions!
Disclaimer: This is an informational post designed to foster discussion. It should not substitute for the advice of your doctor.